normal end tidal co2 dog
In conditions of normal breathing 6 Lmin 12 breathsmin 500 ml for tidal volume etCO 2 is very close to alveolar CO2. Carbon dioxide during ventilation.

Pdf Capnography In Dogs Semantic Scholar
Capnography can be used to measure end-tidal CO 2.

. There was an excellent linear correlation b. Most anesthetics are respiratory depressants and end-tidal CO2 allows early detection of respiratory impairment so appropriate intervention can occur before the problem becomes life threatening. According to the book by Hockenberry and Wilson 2015 p 1140 normal values of ETCO2 are 30-43 mmHg which is slightly lower than arterial PaCO2 35-45mmHg.
The normal levels of expired CO2 in dogs and cats should between 35 and 45 mm Hg millimeters of mercury. End-tidal carbon dioxide ETco 2 monitoring provides valuable information about CO 2 production and clearance ventilation. 2 See Figure 1 p.
Capnography also measures and displays the respiratory rate. However an excess of carbon dioxide in the bloodstream can lead to an abnormal condition causing symptoms ranging from dizziness to convulsions. This is end-tidal CO 2 ETCO 2 which is normally 35 to 45 mm Hg in dogs and 28 to 32 mm Hg in cats.
The normal amount of carbon dixide in the arterial blood is 35-45 mm Hg a measurable unit of pressure. The heart pumps the oxygenated blood to the cells where it is used for normal cellular metabolism. Capnography can be used to measure end-tidal CO 2.
Normal range is 35-45mmHg and roughly correlates with the partial pressure of CO2 in arterial blood remember that PaCO2 is usually slightly higher than ETCO2 by 2-5mmHg. Join us in this hour and learn about monitoring the patient undergoing anesthesia interpretation of end tidal carbon dioxide CO2 values and appropriate interventions for patients with abnormal values. End-tidal carbon dioxide EtCO 2.
The normal end-tidal capnography wave form is basically a rounded rectangle. Common narrow plateaus seen during. The end-tidal level of carbon dioxide is generally less but is reflective of carbon dioxide in arterial blood and can serve as an indirect noninvasive method of assessing the adequacy ventilation.
Left untreated a state of hypercapnia can lead to death. Values for hypercapnia range from 65-75 mm Hg. Oxygen O 2 is inhaled via the lungs where it diffuses across the alveolar-capillary membrane and enters the pulmonary circulation.
The normal capnograph LVFKDUDFWHULHGE D³VTXDUH waveform that plateaus at 30 40 mmHg during expiration and returns to 0 mmHg during inspiration. 1 End-tidal CO2 usually underestimates PaCO 2 by 2-5 mm Hg in mammals. The optimal cutoff PetCO 2 was 18 mm Hg 24 kPa with a sensitivity of 80 and a specificity of 95 at minutes 3 4 5 6 and 8 correctly classifying 91-100 of cases.
Therefore better interpretation of the. Total pressure of a gas is the sum of the partial pressures of the gas Expired CO2 measured PetCO2 mmHg in waveform Percentage Normal Levels PaO2 85-100mmHg PaCO2 35-45mmHg Percentage vs. Examples of some common capnograms are.
Yes the generic normal is considered 35-45. 78 Nitrogen 21 Oxygen 1 CO2 and other gases Exhaled gases. In patients with normal pulmonary function CO 2 normally 35 to 45 mm Hg and ETco 2 should correlate closely with a deviation of about 2 to 5 mm Hg.
48 When a person is breathing out CO 2 the graph goes up. This is an important component of anesthesia because it helps the anesthetist evaluate the patients respiratory rate and also the quality of the respirations breaths. Since problems with lungs are not common and gas exchange between alveoli and the blood is swift and effective.
The end-tidal carbon dioxide tension PetCO2 measured after a single large tidal-volume breath 15 mlkg body weight was compared to simultaneous measurements of PaCO2 in 6 dogs with normal lungs who were receiving high-frequency jet ventilation HFJV. 11172009 4 Measuring End Tidal CO2 Daltons Law. We know that elevated ETCO2 hypercapnia occurs during hypoventilation and a decrease in ETCO2 hypocapnia occurs with hyperventilation.
Anaesthesia of the dog Veterinary Anaesthesia Eleventh Edition 2014 Chapter 15 Pages 405-498. The capnograph is the waveform that shows how much CO 2 is present at each phase of the respiratory cycle and it normally has a rectangular shape Figure 1. Capnography waveforms etCO2 and breathing patterns.
A more complete picture of carbon dioxide transfer can be obtained from a capnogram similar to an ECG tracing. Co 2 Physiology CO 2 is a waste product of normal aerobic cellular metabolism. Expiration 0 40 CO 2 g 20 60 Hypoventilation is characterized by higher than normal end-tidal CO 2 indicating respiratory depression and inefficient gas exchange.
Capnography is the measurement and evaluation of the levels of CO2 in a patients exhaled breath or the end-title CO2 ETCO2. Variants of normal ETCO2 tracings from normal anesthetized animals. 1820 The normal range for ETCO 2 in mammals is 35-45 mm Hg.
MmHg Relate to the air we breath. Circulating blood CO 2 is slightly greater than exhaled CO 2 due to a ventilation-perfusion VQ mismatch.

The Abcs Of Veterinary Dentistry V Is For Ventilation Monitoring
Riding The Wave Of Capnography Understanding Etco2 Vetbloom Blog
Did You Know Hypercapnia Is Synonymous With Hypoventilation
Riding The Wave Of Capnography Understanding Etco2 Vetbloom Blog
Emma Ii Veterinary Capnograph By Dre Veterinary
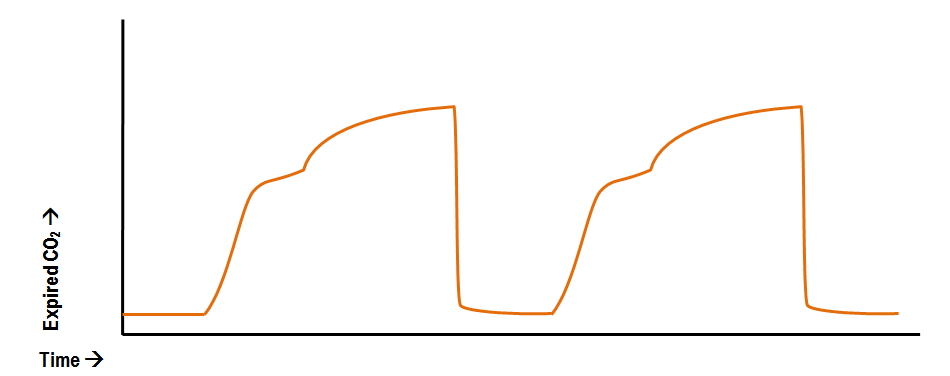
Abnormal Capnography Waveforms And Their Interpretation Deranged Physiology

Veterinary Specialist Services Veterinary Anesthesia

Vetgrad 10 Minute Top Up The Website For Vets

Capnometry In Exotic Animal Species Lafebervet

Why Monitor End Tidal Carbon Dioxide Rwd Life Science
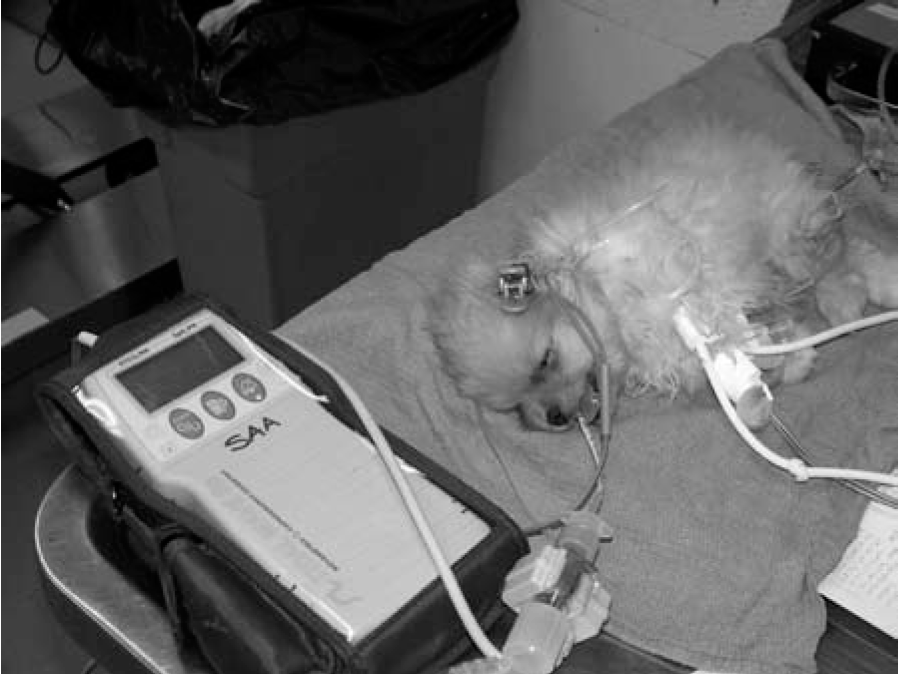
Capnography In Veterinary Medicine Chapter 28 Capnography

Pdf Capnography In Dogs Semantic Scholar

Pdf Capnography In Dogs Semantic Scholar

End Tidal Carbon Dioxide Tension Pet Co 2 In Normal Individuals Over Download Table

